Feeds
A Feed is a stream of data – in our case Product data from a channel – presented in a fixed format using e.g. JSON syntax. Feeds are typically used to make it possible for an external service, like an app or a marketplace tool, to fetch up-to-date information at all times.
A feed consists of:
- A query which selects the subset of your products you want to publish in the feed
- A context section which allows you to select shop, currency & language values and pass them to the query
- A format section where you select which data to include in the feed and how to format it
Each of these components are are explained below.
Query
When you create a feed the first thing you have to do is select a query and configure it (Figure 2.1).
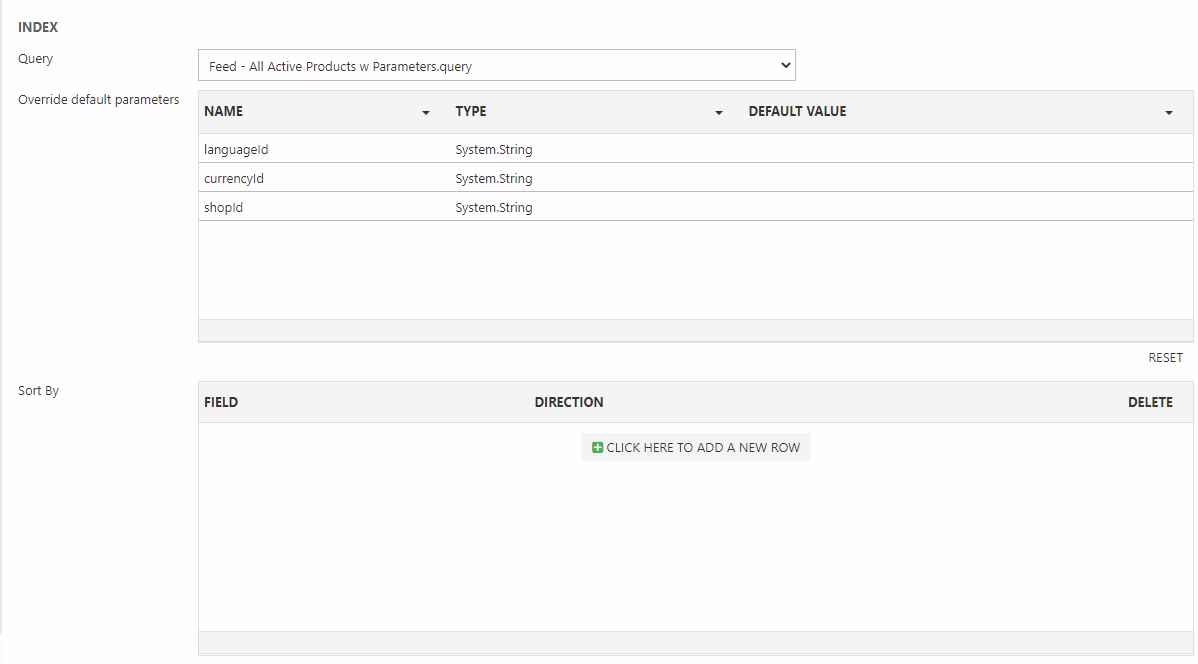
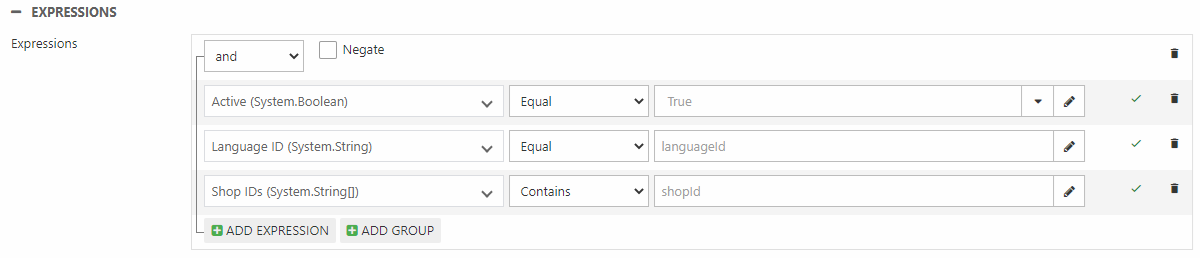
For all intents and purposes you can select any index query, but you should note that if you plan to use the Context section to set the language, currency & shop context the query should be configured to receive the values passed from the feed. This can be done by creating two parameters:
- languageId
- shopId
And, of course, creating the expressions using them (Figure 2.2).
Context
The context section (Figure 3.1) is used to set the feed context when retrieving product data and looking up prices and variants.
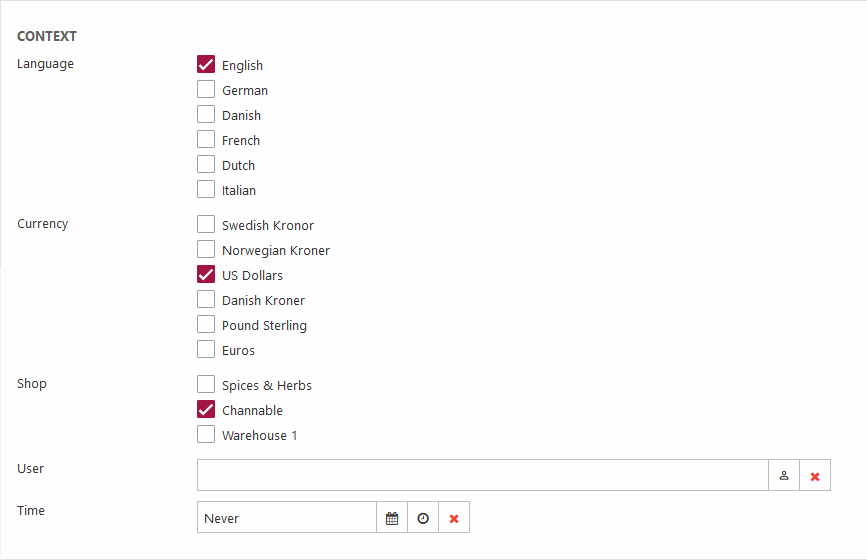
You can select the following:
|
Parameter |
Use |
Notes |
|
Language |
Select the ecommerce language(s) to include in this feed |
Make sure the index querty has a languageId parameter and an expression using it. |
|
Currency |
Select the currency you want the feed to use |
|
|
Shop |
Select the shop/warehouse/channel |
Make sure the index query has a shopId parameter and an expression using it. Typically you want to select a channel with a structure that corresponds to the service you’re integrating with. |
|
User |
Select a user to pass to the webapi |
Typically used to fetch customer-specific prices on solutions using the price matrix. |
|
Time |
Set a specific time to use in price calculations | Typically used to fetch future prices |
Format
The Format section is used to control two things – which data to include in the feed and how to render it. In practice this is done by selecting a feed provider and configuring it:
|
Provider |
Used for |
Comments |
|
Template feed provider |
Generating custom feeds using a ViewModel template |
To use:
An URL to the feed will be generated, and can be visited/used externally. |
| XML feed provider | Generating XML feed data - and (optionally) transforming this data using an XSLT stylesheet. |
To use:
|
Feed Content
When you save a feed, one or more API URLs to the feed will be generated (Figure 5.1) - click these to review the current feed output in a new tab. Each URL is listed with their selected options, which the feed is based on.

The API URLs can be extended with custom parameters, provided that the repository query is set up to receive them. Simply add the parameter to the querystring and pass values to it:
You can also set up a scheduled task which saves the contents of a feed in a file - see here.
