Basic Website SEO
Website SEO is the process of optimizing a website so it ranks higher in search engine results, leading to more relevant organic traffic. So how do you optimize a website for search engines? Well, mainly by producing quality content which makes you visitors stick around – but there’s a little more to it, and you can find some help in our Essential On-Page SEO article.
In this article we will cover some of the things you can do at the website level – some of them will be handled by us, others are up to you.
We will be covering:
- Lighthouse
- Google Search Console
- Redirects
- Image optimization
Lighthouse
Lighthouse is an open-source, automated tool for improving the quality of websites. It is very helpful for SEO purposes, because the reports it generates include several SEO-related checks which you can then either cross off or fix for any given page. You should, of course, use Lighthouse continuously during development to find and fix potential issues early.
Lighthouse can be run in a number of ways – e.g. as a Node module – but the easiest it to use Chrome Devtools (inspect in Chrome):
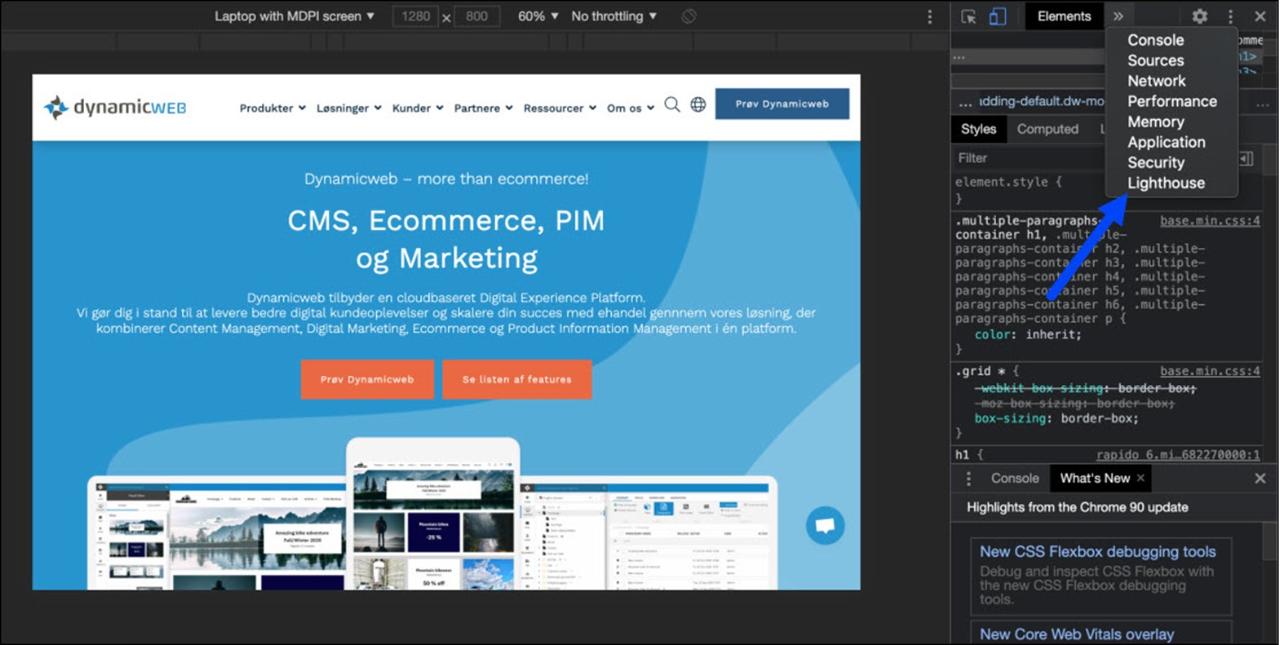
- Right-click the page and choose ‘Inspect’
- Select the Lighthouse tab (dock to bottom) or click on the area selector in the corner and choose ‘Lighthouse’ (dock to right/left) (Figure 2.1)
- On the lighthouse tab, cross off the categories you want to check and click ‘Generate report’ (Figure 2.2)
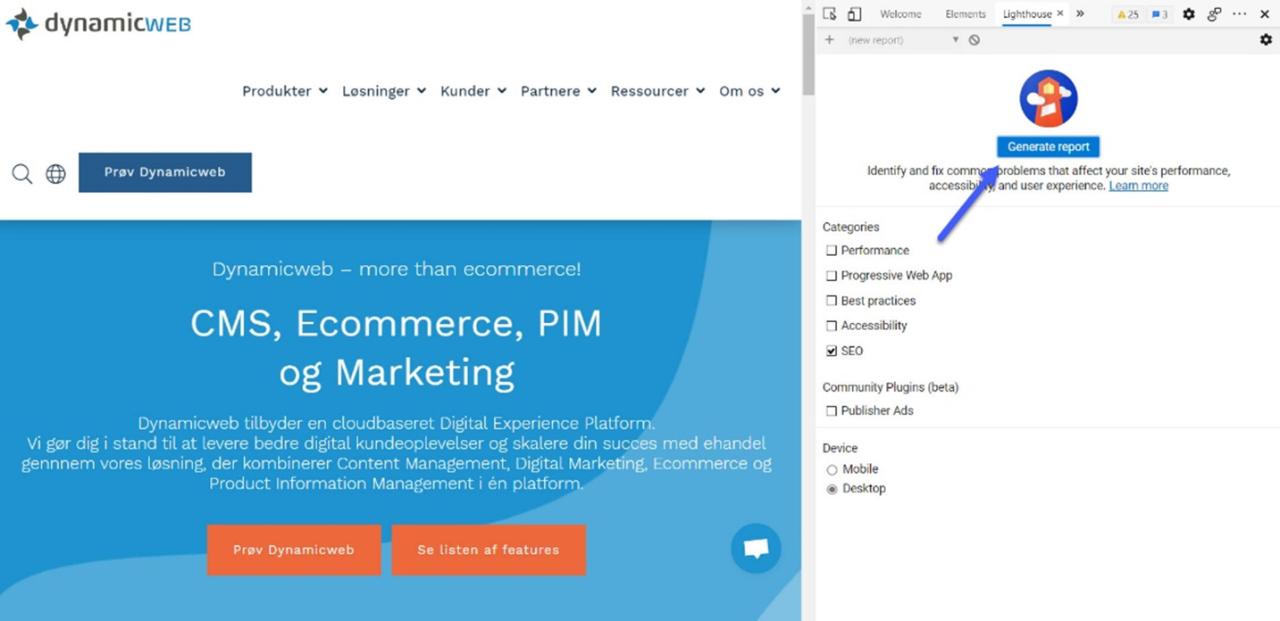
- Lighthouse will now run a series of tests and generate a report with a suggestion and a total SEO score for the website
At the time of writing, the following audits are run:
|
Audit |
What it checks |
Notes |
|
<meta name=”viewport”> |
Checks that the document has a <meta name=”viewport”>-tag with width or initial-scale |
Viewport is the user’s visible area of the webpage. The tag is used so webpages fits screens responsively and is especially used to optimize mobile screens
|
|
<title> element |
Checks that the document has a <title> element |
The title gives screen reader users an overview of the page, and search engine users rely on it heavily to determine if a page is relevant to their search. |
|
Meta description |
Checks that the document has a meta description |
Meta descriptions may be included in search results to concisely summarize page content. |
|
HTTP status code |
Checks that the page has a successful HTTP status code |
Pages with unsuccessful HTTP status codes may not be indexed properly. |
|
Descriptive text for links |
Checks that links has a descriptive text |
Descriptive link text helps search engines understand your content. |
|
Crawlable links |
Checks that links are crawlable |
Search engines may use `href` attributes on links to crawl websites. Ensure that the `href` attribute of anchor elements links to an appropriate destination, so more pages of the site can be discovered. |
|
Blocked webpages |
Checks that page isn’t blocked for indexing |
Search engines are unable to include your pages in search results if they don't have permission to crawl them |
|
Valid robot.txt |
Checks that the page have a valid robot.txt |
If your robots.txt file is malformed, crawlers may not be able to understand how you want your website to be crawled or indexed |
|
Alt-attributes for images |
Checks that there are alt-attributes for images |
Informative elements should aim for short, descriptive alternate text. Decorative elements can be ignored with an empty alt attribute |
|
Valid hreflang |
Checks that there is a valid hreflang |
hreflang links tell search engines what version of a page they should list in search results for a given language or region |
|
Document avoid plugins |
Checks that documents avoid plugins |
Search engines can't index plugin content, and many devices restrict plugins or don't support them |
Some of the SEO audits are related to formal On-page SEO such as <title>-element and meta-description. You will also notice that many of the SEO-related audits checked by Lighthouse are handled natively in Dynamiweb Swift – and as such you don’t have to worry about them unless you’re customizing your Swift-solution.
Apart from the SEO-related audits it also checks for performance, accessibility, and best practice issues – all of which will indirectly impact your search engine ranking. Remember, you want the user to spend time on your website as this will indicate to search engines that it is useful to the visitor.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free service which monitors, maintains, and troubleshoots a website in relation to search results. It is a very useful tool if you want to understand how Google sees a website – and use that knowledge to improve your SEO.
You can get started with Google Search Console here – or visit the official documentation.
Please note that one of the things you can do is submit a sitemap to google search console. Dynamicweb automatically generates a sitemap on all websites with a public URL.
Redirects
Another important thing to be aware of is redirects – when used properly, redirects will help you maintain your Google ranking even when highly-ranked pages are unpublished.
Basically, a redirect sends a visitor to a different page than the page they requested. This is especially important when you want to:
- Delete pages with high SEO value
- Switch domain names
- Merge websites
And, of course, fix broken URLs.
To create redirects you can use the built-in Redirects tool – keep these things in mind:
- Always redirect to relevant pages
Google is only interested in showing the most relevant results, so do not redirect to irrelevant pages as it can cost you rankings and organic traffic. - Avoid redirecting loops
Make sure all your redirects point directly to another active URL and not to a redirected page. If you redirect to a redirected page loops appear, which can negatively affect page speed. - Mind the redirect type
The most SEO-friendly redirect is the 301-redirect type, which signifies permanent URL redirection and informs search engines of the permanent move. Of course, you should only use this type if the redirect is permanent.
Image Optimization
How long it takes for a page to load has a definite impact on search engine rankings. You should therefore always make sure your website loads as quickly as possible – here is some general advice:
- Keep images below 500 KB with a width between 1500px to 2500px.
- Whenever possible, use the .jpg image file type. Limit gifs or animations.
- If a page is larger than 5 MB, removing content or reducing the size of your images can help it load faster.
