Data Integration Module
The Data Integration module lets you import and export data to and from Dynamicweb.
In general terms, the module lets you create activities which accomplish a particular task – e.g. export all your users to an XML file, import user from your CRM, and so forth.
An activity consists of a source provider and a destination provider to match the intended task (Figure 1.1) – if exporting users to XML, for instance, you will use the user provider as the source provider and the xml provider as the destination provider.
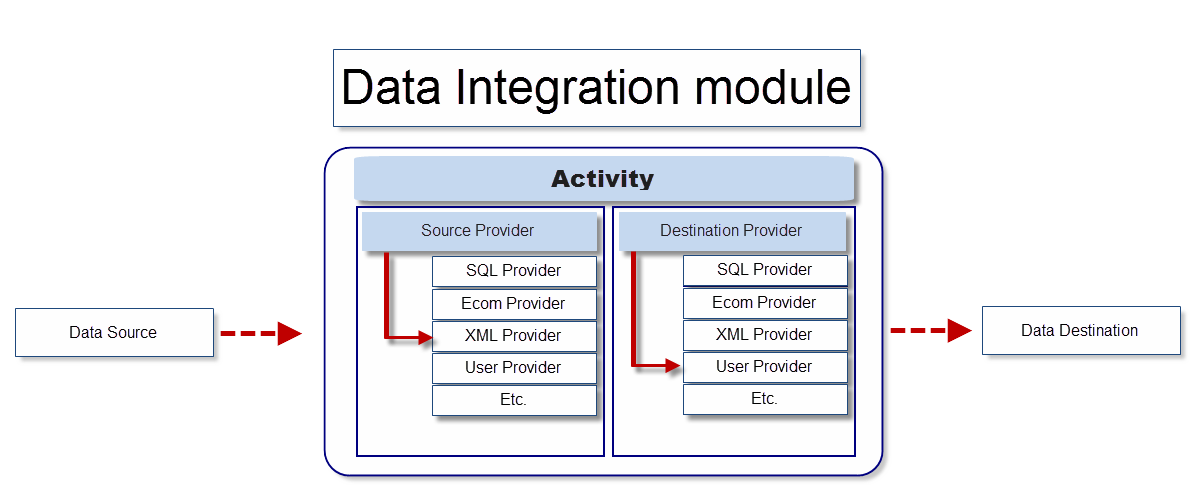
Dynamicweb ships with a number of built-in providers, most of which can function as both a source and a destination provider.
|
Provider |
Can be source? |
Can be destination? |
Description |
|
Dynamicweb Provider |
YES |
YES |
Complex to setup, but can access the full Dynamicweb database. High performance – but you need to know the Dynamicweb database to get things right. |
|
Dynamicweb Provider with Views |
YES |
NO |
Same as Dynamicweb Provider, but with support for SQL Views. |
|
SQL Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data directly to and from a Microsoft SQL server database. |
|
SQL Provider with Views |
YES |
NO |
Same as SQL Provider, but with support for SQL Views. |
|
User Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export user and user group data in a more straightforward manner than the Dynamicweb provider. |
|
Excel Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data to and from Microsoft Excel. |
|
CSV Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data from and to CSV files. |
|
XML Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data from and to XML files. |
|
CRM Provider |
YES |
NO |
- |
|
Ecom Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export ‘incomplete’ data to and from the Dynamicweb database, able to e.g. auto-assign IDs to imported products and groups. Memory overhead: roughly XML file size x 3. |
|
Item Provider |
YES |
YES |
- |
|
Order Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export order and orderline data to and from the Dynamicweb database |
This means that you have a large degree of freedom out of the box when moving data in and out of Dynamicweb – and you can of course also create custom providers.
Requirements
The Data Integration module requires an underlying database running on Microsoft SQL Server 2008 or later.
Additionally, your webserver must be able to resolve its own name from DNS; after calling jobrunner.aspx a new thread is created to another .aspx, where the job is actually executed. So if you have http://website.com, the IIS-server should be able to resolve website.com, as it will be calling ‘http://website.com/JobRunnerBackground.aspx?’.
Basic Concepts
In this section you will learn about:
- The Data Integration area
- How to create and run an integration activity
- The integration details view – and how to use conditionals and scripting to control your import/export process
The Data Integration area
Your Data Integration module activities are created and managed from the Data Integration area (Figure 3.1) – which can be accessed by going to Management Center > Integration > Data Integration.
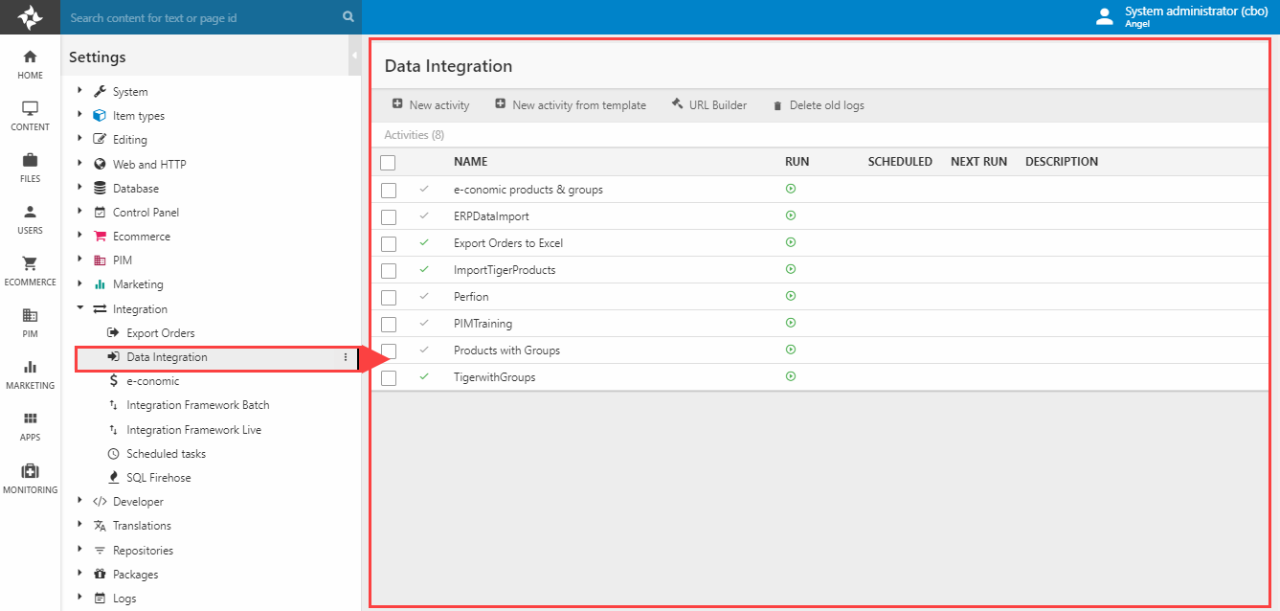
From the Data Integration area you can:
- Create new activities
- Create new activities from a template
- Open the URL builder
- Delete old logs
- View and edit existing activities – and run them!
Read more below.
Creating an activity
Creating a new integration activity is both trivial and complicated at the same time.
It’s trivial in the sense that clicking New activity will open a wizard which will take you through all the steps:
- Select and configure a data source provider
- Select and configure a data destination provider
- Select the tables to import or export data from
- Name the activity
- Check the column mappings
- Save and Run the activity
And that’s it. So mechanically, everything is pretty straight-forward – the complexity comes from the fact that you need to know what you want to do.
“New activity from template”
If you use the Integration Framework, some of the common import/export jobs have already been defined for you in (customizable) templates. To learn more, get acquainted with the Integration Framework.
Selecting source and destination providers
Normally, you’ll be approaching the Data Integration module with a pretty clear idea of what you want to accomplish.
With that in mind, selecting (and configuring) the right source and destination providers becomes much easier.
The built-in providers supplied by Dynamicweb are:
|
Provider |
Can be source? |
Can be destination? |
Description |
|
Dynamicweb Provider |
YES |
YES |
Complex to setup, but can access the full Dynamicweb database. High performance – but you need to know the Dynamicweb database to get things right. |
|
Dynamicweb Provider with Views |
YES |
NO |
Same as Dynamicweb Provider, but with support for SQL Views. |
|
SQL Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data directly to and from a Microsoft SQL server database. |
|
SQL Provider with Views |
YES |
NO |
Same as SQL Provider, but with support for SQL Views. |
|
User Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export user and user group data in a more straightforward manner than the Dynamicweb provider. |
|
Excel Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data to and from Microsoft Excel. |
|
CSV Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data from and to CSV files. |
|
XML Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export data from and to XML files. |
|
CRM Provider |
YES |
NO |
- |
|
Ecom Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export ‘incomplete’ data to and from the Dynamicweb database, able to e.g. auto-assign IDs to imported products and groups. Memory overhead: roughly XML file size x 3. |
|
Item Provider |
YES |
YES |
- |
|
Order Provider |
YES |
YES |
Import and export order and orderline data to and from the Dynamicweb database |
So consider the task you want to accomplish and make the appropriate selection.
Here are a couple tips and tricks to help you get started:
- 9 out of 10 times your source for import will be XML, but occasionally Excel or CSV is useful for end-users to work with. XML is also a very popular destination format.
- If you import data to Dynamicweb, it usually makes most sense to use the Dynamicweb Provider as the destination provider – but in some cases the specialized providers may be useful:
- The Ecom Provider allows you to import incomplete product data and have the provider auto-assign the missing values. Comes with significant memory overhead.
- The User Provider contains options for e.g. removing inactive users, generate passwords for new users, and notifying new users by email after import.
- The XML Provider lets you use XSL transformation files to modify either your source or destination XML – this can be very useful. The downside is that you need to work with XSLT.
You can read more about each provider in the individual provider articles – or read about creating custom providers.
Selecting and mapping tables
The entire import/export tool is built around the concept of mapping tables to tables, and between those tables, mapping columns to columns. This approach is modeled closely on the approach taken by the Microsoft SQL Server Import and Export Data Tool.
After selecting a source and destination provider you will be asked to select source tables (Figure 6.1) and map them to destination tables.
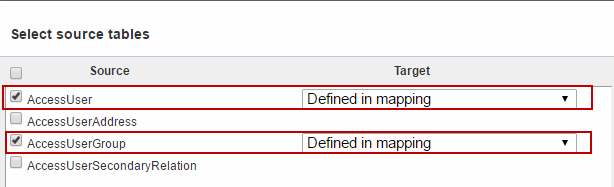
In this case, I export data to an XML file, and so I cannot select a target table (as the destination file does not exist yet). However, if your destination is a database you will be able to select a target table here. If your destination table has the same name as the source table, it will be automatically selected in the dropdown.
Once you’re happy with your table selection and mapping click finish – you will be prompted to name the activity (Figure 6.2). Do so.
Automatic mapping on run will be explained in the next section.
It is VERY IMPORTANT that a table definition is only defined ONCE per activity. So if your source is a folder with multiple XML files for importing Ecommerce data, the table EcomProducts must only be referenced once. If you need to import data to the same table destination more than once, you should split your import into multiple activities.
Column mapping
After naming the activity, you can create or review the column mappings for each table in your import/export (Figure 7.1).
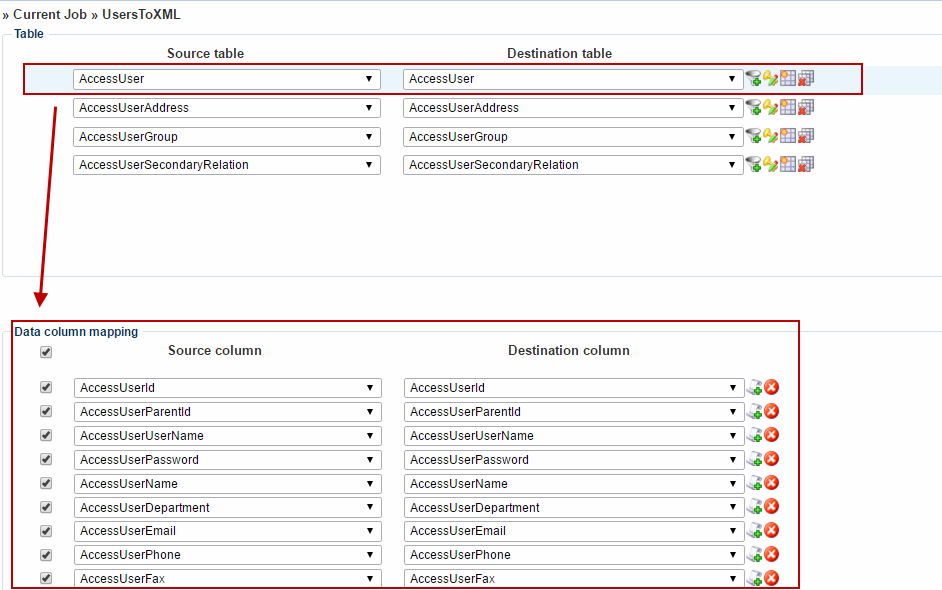
As with source and destination tables, if the column names in the destination table matches those in the source table the mappings will be created automatically.
From the column mapping overview, you have access to a number of advanced options for handling and modifying your import/export activity.
For instance, you can:
- Remove columns (e.g. AccessUserPassword and other sensitive data) which should not be imported or exported
- Add a conditional filter to a table mapping to e.g. export only products with a stock value below 10
- Customize key settings
- Use scripting to prepend or append something to column data, or replace the source data with a constant
Read more about scripting and conditionals below.
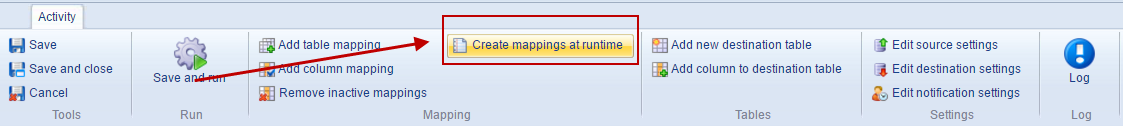
Create mappings at runtime/Perform mapping automatically on run
During the creation of a new activity you have the option (during the naming-step) to check a perform mapping automatically on run checkbox, and from the ribbon bar of the activity details view you have access to a create mappings at runtime button (Figure 7.3).
If either of these are active, Dynamicweb will automatically generate mappings between source and destination columns with the same name every time an activity is run.
This makes it less cumbersome to add custom fields and import data to them – as long as the names match, it will be done automatically.
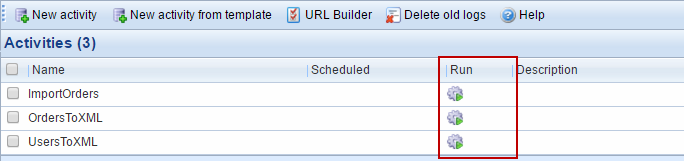
Running an activity
Activities may be run by clicking the icon in the run-column of the data integration overview (Figure 8.1).
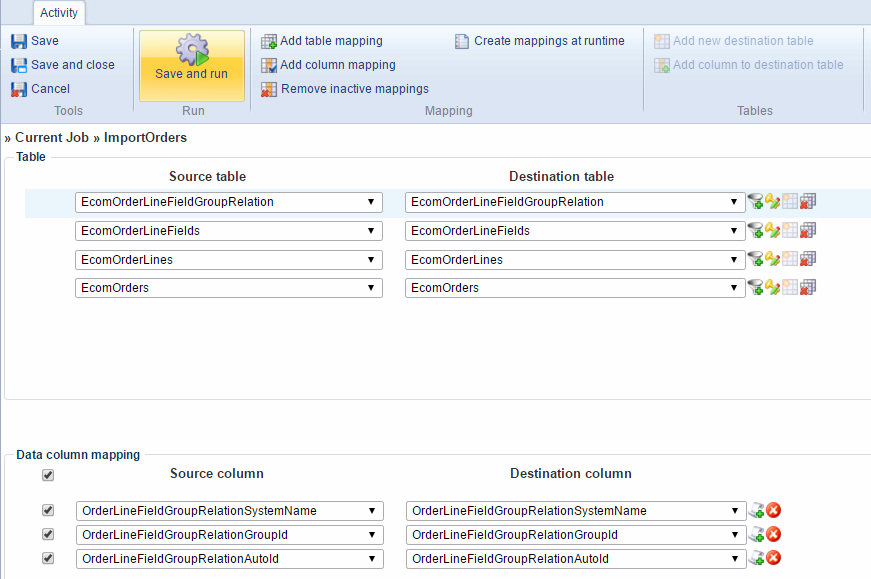
You can also run an activity by clicking the Save & Run button from activity details view (Figure 8.2), either during creation or when viewing or editing the activity details.
Scheduling an activity
In some cases, it makes sense to schedule an activity to be run at a predefined interval. This is done using the standard Scheduled task functionality in Dynamicweb.
To set up a schedule for an activity, right click the activity in the Data Integration area view and click Schedule task (Figure 9.1).
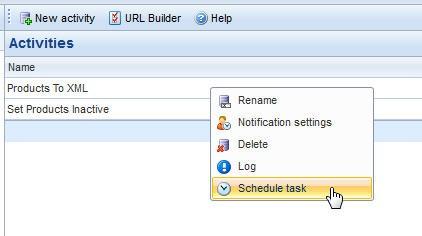
Create a scheduled task by selecting a start date and interval in the standard manner.
Scheduled integration activities are run by accessing an auto-generated activation URL – you can access the URL when editing a scheduled task for an integration activity.
The same type of URL can be generated manually and used to run an activity remotely – read more below.
On scheduled tasks
The Scheduled Task function in Dynamicweb relies on Windows scheduled task. This is provided by our hosting partner Hostnordic, but if you are hosting elsewhere (or in your own hardware), make sure you have Windows scheduled task configured. Use Curl.exe to trigger http://yoursite.com/Admin/Public/TaskExecute.aspx every 5 minutes.
Running an activity remotely (URL Builder)
In some cases, it may be necessary to run an import/export job remotely. This happens by calling a job runner via an URL.
The job runner takes two parameters:
- Job(s) to run
- Token
The job parameter is a comma-separated list of jobs and the token is a unique checksum to prevent unwanted execution.
To generate URLs for remotely running an activity, use the URL Builder tool which is accessible from the Data Integration area view (Figure 10.1).
Using the URL Builder tool you can:
- Select one or more activities (jobs) to run – move them to the right column
- Click generate URL to generate an URL for running the currently selected activities. The installation checksum (see System Information) will be added to the token parameter.
- Click Create as a scheduled task to do so – this lets you create a single scheduled task which runs more than one activity at the same time
Each individual activity is run sequentially, as a single transaction.
If the ‘Stop on failed jobs’ checkbox has been checked, the activity will stop if an activity is not completed correctly. Already completed activities will not be reversed – i.e. the data from activity 1 is still imported/exported, even if job 2 fails.
Synchronous execution
You may have noticed the checkbox for enabling synchronous execution in the screenshot above.
Normally, the URL Builder generates an “ordinary” execution based on an asynchronous call that passes the activity to a new thread and proceeds in the background.
However, this means that you will not know the actual success/failure of the activity (without using email notifications or consulting the log).
For automated activities, this is not always good enough – and so you can call the alternate JobRunnerSynchronized.aspx instead, which awaits the response of the actual activity execution.
The up-side is that you will know the real success/failure status of the executed job straight away. The down-side is that you should be very aware of the amount of time you have to wait for the response, in order to avoid a potential HTTP Request timeout.
If executed successfully in browser you'll get a content of "See log file: yourjob[date]-[timestamp].log.".
If job succeeds you get a HTTP 200 in return. If job fails a HTTP 500 is returned.
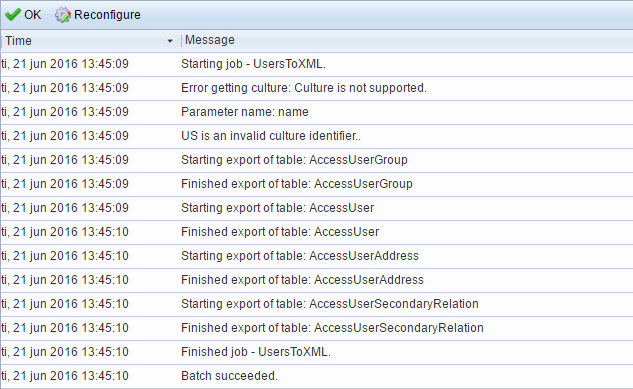
Activity log
Once an activity has been run you will be presented with a log of how everything went (Figure 11.1).
Additionally, you have access to both the latest log and historical logs from the activity details view – simply click the log button to bring up the log overview (Figure 11.2).
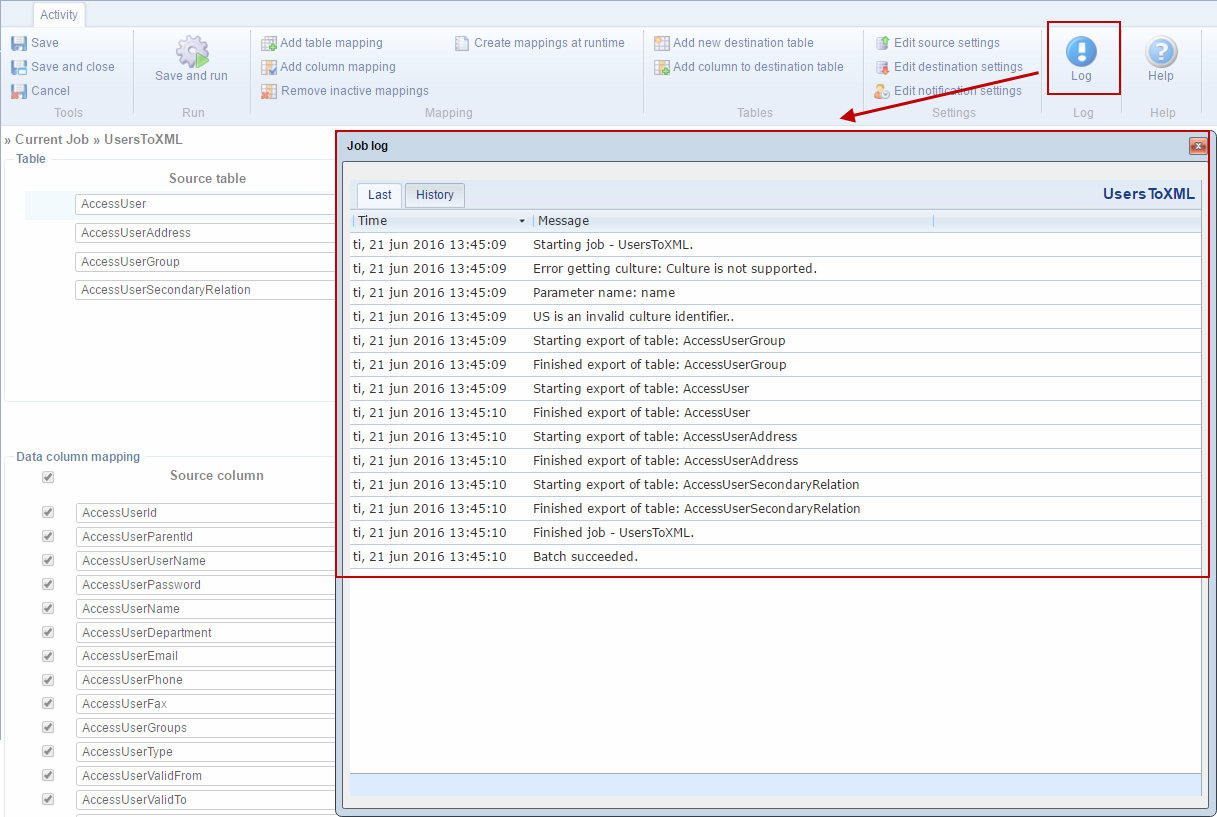
Physically, logs can be found in the /System/Log/DataIntegration folder.
Notification settings
Often, it may be useful to email key people the result of an activity after it’s been run – especially if it fails!
To set up email notifications right-click on the activity in the Data Integration area overview and click Notification setting (Figure 12.1).
This opens the notification settings for the activity (Figure 12.2).
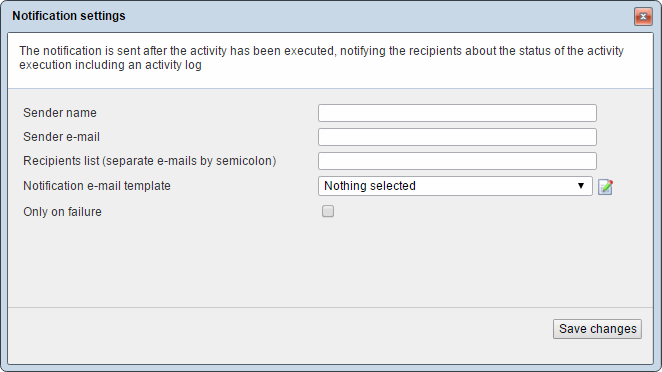
To set up email notifications for the activity:
- Specify a sender name and sender email
- Add the emails of the intended recipients – separate emails by semicolon if more than one
- Select (or edit/create) a notification email template
If you want to limit email notification to only failed activities, check the only on failure checkbox.
The activity details view
By clicking an existing activity in the Data Integration area, you can open (and edit) the activity details and settings.
For that purpose, you have access to a ribbon bar (1) and table/column mappings area (2) (Figure 13.1)
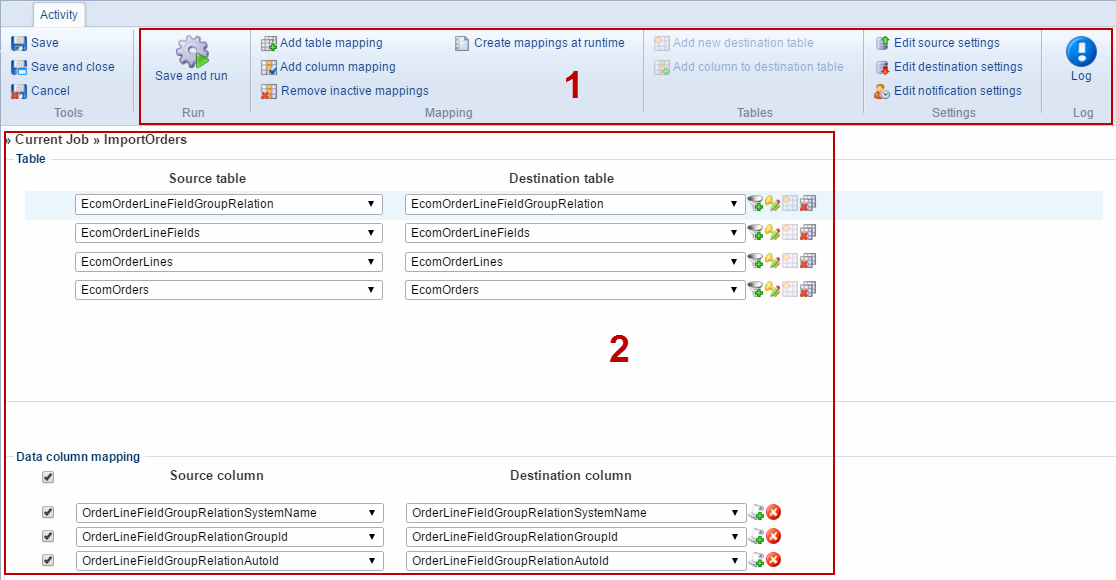
Using the ribbon bar you can:
- Save and run and activity
- Add table and column mappings, remove inactive mappings – or activate the create mappings at runtime option
- Add a new destination table and add columns to a destination table
- Edit the source provider and destination provider settings
- Edit or configure email notification settings
- Access the most recent log file – or review old log files
From the table & column mappings view, you can:
- Use conditionals to filter rows during import/export
- Use scripting to append or prepend something to an input value, or to replace input with a constant
- Customize key values
Read more below.
Conditionals
When mapping tables, you can use conditional to filter which rows should be affected during import/export – e.g. if you want to export all products with a stock value lower than 10.
To set conditionals, click the conditional icon next to a table mapping in your activity overview (Figure 14.1).
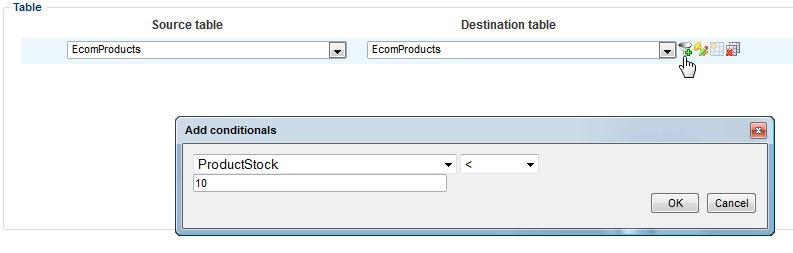
In addition to comparing simple values, you use @NULL to match on true DbNull (isNull = “true” in the XML) and @NULLOREMPTY to match null and empty strings (e.g. “” or <! [CDATA[]]> in the XML).
Applying conditions dynamically
In some cases it may be useful to run an activity with dynamic parameters. For instance, you may want to retrieve orders within a particular date interval, a particular order state, or with a specific order total.
To do so add a conditional using the following syntax:
- {{ParameterName||”value”}}
Where ParameterName is the name you want to give the parameter which is passed to URL and “value” is the default value you want to pass on (Figure 14.3).
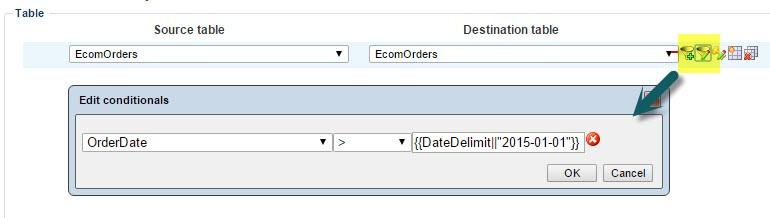
Scripting
During column mapping, you can use scripting to append, prepend or set constants when the activity is run.
To do so click the scripting button to the right of a column mapping – this opens the scripting pop-up (Figure 15.1).
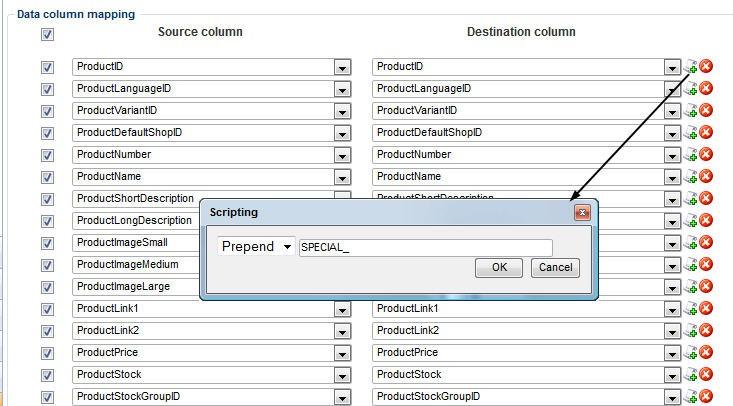
Simply select append, prepend or set constant as appropriate – and enter the value you want to append/prepend/create.
Set Constant is mainly used if you want to replace all source values with the constant, or (more likely) to create a destination column with no source column available, e.g. if your ERP system has no language context column and you want to import these products into a LANG1 or LANG2 context in Dynamicweb Ecommerce.
Custom keys
Keys in data integration are similar to Primary Keys in databases. These are used to determine when a new row should be added, and when an existing row should be updated.
Clicking the "Set keys" icon (Figure 16.1) will pop up a window where you can choose the key settings that should be considered upon import

Default will be the actual key(s) of the column. For instance, the default key settings for table EcomProducts is the composite key ProductID + ProductLanguageID + ProductVariantID. However, in some cases you may want to set the unique identifier to ProductNumber.
Implementing
In this section, you will learn about:
- Moving Data Integration activities to other solutions
Moving activities to other solutions
Data Integration activities are store as XML files on a solution, and can be accessed through the file manager.
To move an activity to a different solution, simply move the activity from /Integration/Jobs on one solution to /Integration/Jobs on the target solution (Figure 18.1).
Please note that all paths to source files (CSV or XML) are static in the activity file and must be manually adjusted if they differ on the destination solution.
Similarly any custom fields / tables mapped in the job file will need to be recreated. However as the database schema is validated on job load you will be informed of any potential errors.
Data Integration notifications
Data Integration notifications contains only one JobFinished notification which is raised after the Data Integration job execution is finished. JobFinished notification allows access to information about the job execution, log file and the tables present in the job. JobFinished notification is located in the Dynamicweb.DataIntegration.Integration.Notifications namespace.
The following example shows how to create a JobFinished notification subscriber:



